What is DNA barcoding?
The thing they don’t tell you:
Science can be cool.
As I go into my third year at Florida Tech, I’ve been able to work in three different labs assisting with research; I don’t think many undergrads at other universities could say that.
The opportunities available to me have been astounding and I even have my name on a submitted paper. The field of science has always captivated me and I knew that this idea of endless discoveries was what I wanted to be doing the rest of my life. Science has the ability to learn new things about the past, the present, and the future. Yet my engineering major friends still won’t believe me when I say science can be cool.
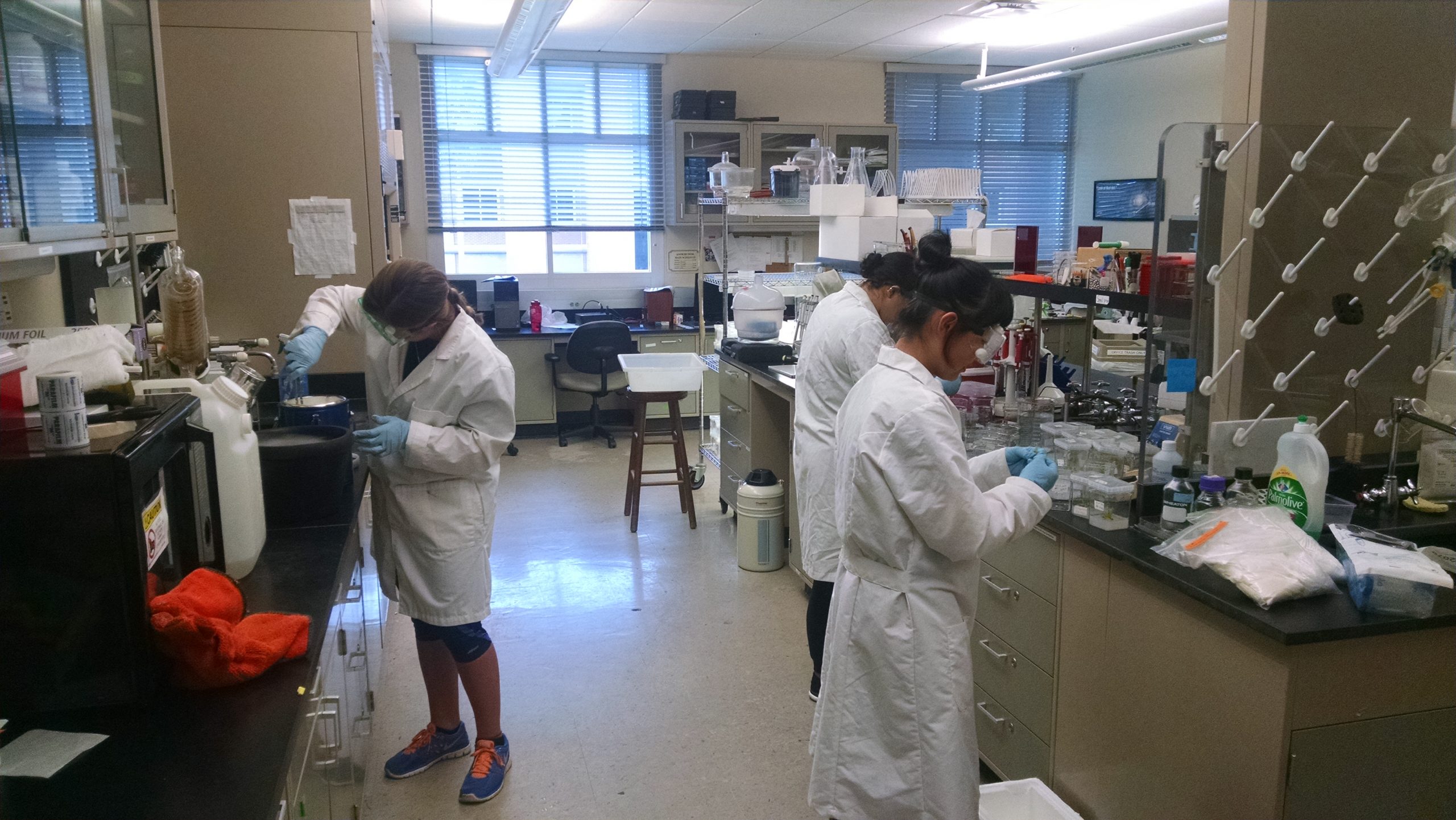
This semester I started working in the Plant Biochemistry Laboratory. The project I’m working on is using DNA barcoding on single pollen grains as a way to increase species classification accuracy.
What is DNA barcoding?
Well, let me explain…
Barcoding w orks the same way as a barcode on the back of a cereal box in the grocery store. In genetics, this barcode is a short DNA sequence in a certain part of the genome of an organism. Just like in the store how the barcode tells the system what the item is, a genetic barcode can identify a species. With pollen grains, the specimen is so small that it can not be seen with the naked eye. Instead, to see the grain it must be examined under a microscope.
orks the same way as a barcode on the back of a cereal box in the grocery store. In genetics, this barcode is a short DNA sequence in a certain part of the genome of an organism. Just like in the store how the barcode tells the system what the item is, a genetic barcode can identify a species. With pollen grains, the specimen is so small that it can not be seen with the naked eye. Instead, to see the grain it must be examined under a microscope.
As you can imagine, it’s slightly difficult to identify the family of a grain, let alone the species. Currently, this identification is done by expert palynologists (people who study pollen) who look at the visual characteristics of a grain such as the shape or the surface pattern. Unfortunately, this leaves much up to interpretation. Cue barcoding – By looking at the same region of DNA in each pollen grain, there is enough variation between species to tell the difference. Crazy right?
So now I bet you’re asking: “Why do I care?” Well, there are a number of reasons why barcoding is cool.
• For starters, DNA barcoding is a great tool for conservation efforts. Biodiversity, which is the variety of life on earth, helps scientists to understand the interactions between species and habitats. Understanding these interactions can help to increase survival in endangered species as well as to get a better grasp on whats causing these declines in certain species.
• Barcoding can also aid in the discovery of new species. At this point in time it is thought that only 15% of the species have been discovered and it is estimated that there are around 8.7 million species on earth! Because the differences in many species are not visual, their genetics are what sets them apart.
• One more benefit to barcoding can be found in forensics. This application ranges from identifying species involved in animal trafficking, to plant trafficking, to mislabeled foods. Not only can it help law enforcement but it could be pretty important for consumers as well. If you’re looking for a cool read, check out this link: How DNA barcodes can beat the wildlife traffickers.
The goal in our lab is to be able to use the barcodes of single pollen grains to  model a geographic distribution of certain species. This would assist in all the categories I listed above and as the methods develop, there may be even more applications.
model a geographic distribution of certain species. This would assist in all the categories I listed above and as the methods develop, there may be even more applications.
It’s like all the crime shows like Bones and CSI where they put a soil sample into a computer and are able to tell where the criminal was. The technology is close, and the science is ‘oh so cool’.